In today’s market, consumers anticipate a seamless and adaptable shopping experience that spans various channels and touchpoints, such as websites, stores, mobile apps, and social media. Meeting these expectations requires brands to ensure precise and uniform product information is delivered consistently across diverse sales channels.
According to Gartner’s Research, it has been found that organizations dealing with poor data quality, cost them $12.9 million per year and increases the complexity of data ecosystems which leads to poor decision making.
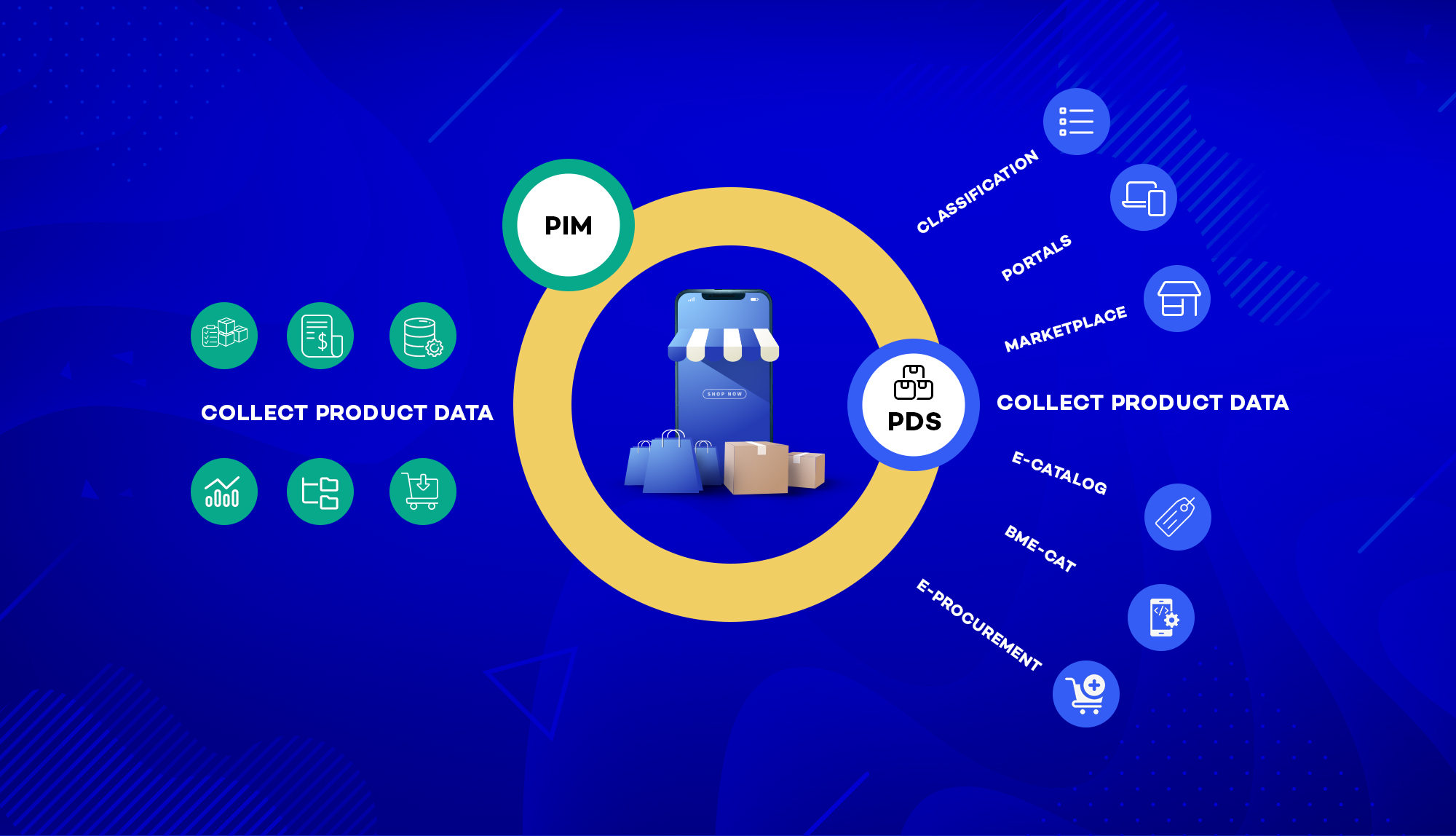
To rectify the entire ecosystem, data syndication comes into play. It forms the foundation of trust in eCommerce, vital for implementing an omnichannel strategy that ensures a seamless and consistent shopping experience.
What is Product Data Syndication?
Product data syndication involves distributing accurate and relevant product information across various digital channels, including websites, marketplaces, and social media.
Manual management of this process, especially for brands with omnichannel strategies, can lead to errors and inefficiencies. But with Product Data Syndication you can simplify and automate this, ensuring consistent and precise product information delivery.
According to Salsify Consumer Research Report, approximately 31% of users said “not enough information or product detail incomplete” as their primary reason for not purchasing online.
Advanced PIM solutions with built-in syndication capabilities further enhance this process by providing a centralized source of truth for product data. Combining PDS and PIM technologies enables organizations to optimize their syndication needs and maintain data accuracy across the digital shelf.
Why Product Data Syndication is Important for Brands?
Sustainable growth depends on scalability, and as operations expand, the volume of data inevitably increases. For brands, manufacturers, or retailers navigating the vast e-commerce world, the potential advantages of PDS strategy may not be fully realized.
To assess whether your company could gain value from product data syndication, consider comparing your challenges with the six key challenges commonly faced by single-channel brands.
- Scaling Challenges: Are you finding it difficult to meet the growing demand for accurate and compelling content across both new and existing channels?
- Branding Disparities: Is there inconsistency in the contextualization, relevance, and uniformity of your product stories and enriched content across various channels?
- Delayed time-to-market: Are data maintenance, validation, and endpoint compliance acting as significant impediments to timely product launches?
- Inefficient Workflows: Is your organization effectively automating processes, allowing internal resources to focus on strategic tasks rather than constant digital shelf management
- Eroded Customer Loyalty: Is your brand consistently exceeding customer expectations from the initial contact to the post-sale phase?
- Disconnected Touchpoints: Can you confidently assert that your product information maintains 100% consistency across every channel and platform? If your brand encounters difficulties in any of these areas, the adoption of a product data syndication will bring significant advantages to your operations.
Key Aspects of Effective Data Syndication
Here are some key aspects of product data syndication that becomes paramount for several compelling reasons:
1.Consistency Across Channels:
Consistency is vital in effective data syndication. Maintaining uniform and accurate product information across digital platforms, such as websites, marketplaces, and social media, builds consumer trust, enhances the brand experience, and reduces the risk of errors, ensuring a reliable customer journey. This consistency not only fosters a cohesive brand image but also mitigates the risk of errors or discrepancies in pricing, descriptions, and other critical information, ultimately contributing to a seamless and reliable customer journey across all touchpoints.
2.Automated Distribution:
Automated distribution is a key element in product data syndication, streamlining business operations by automatically disseminating products, information, or content across various channels. This relies on technology to manage tasks like inventory, order fulfilment, and data syndication without manual intervention. Automation enables organizations to boost speed, accuracy, and overall effectiveness in reaching target audiences, optimizing distribution workflows, and enhancing customer experiences.
3.Customization for Different Channels:
Customization for different channels in data syndication refers to tailoring content, messaging, or product information to suit the unique characteristics and requirements of various marketing or distribution platforms. This strategy recognizes that each channel, such as websites, social media, or marketplaces, has distinct audience expectations and engagement dynamics. By adapting content to resonate with the specific preferences and formats of each channel, businesses can maximize the impact of their messaging, optimize user experiences, and effectively cater to the diverse needs of their target audiences across various digital touchpoints.
4.Scalability and Flexibility:
Scalability and flexibility are fundamental attributes in the data syndication operations. Scalability refers to a system's capacity to handle growth and increased demands, adapting seamlessly to expanding requirements. Flexibility, on the other hand, pertains to the ability to modify or adjust processes to accommodate changing circumstances or evolving business needs. Together, these traits empower organizations to navigate dynamic market conditions, efficiently manage increased workloads, and readily adapt to new opportunities, ensuring a robust and adaptable foundation for sustained success and growth.
5.Real-Time Updates:
Real-time updates involve the instantaneous and continuous dissemination of information or changes, ensuring that the most current data is available at any given moment.
In various contexts, such as technology, communication, or data management, real-time updates enable users to access the latest information without delays. This capability is particularly crucial for maintaining accuracy, responsiveness, and relevance, allowing organizations to make informed decisions, provide up-to-date content, and enhance overall efficiency in dynamic and fast-paced environments.
6.Feedback Loop Integration:
Feedback loop integration refers to the systematic incorporation of feedback mechanisms into a process or system. In the context of business, marketing, or product development, it involves creating a continuous cycle where feedback from customers, users, or stakeholders is collected, analyzed, and used to inform future decisions or improvements.
This approach fosters a dynamic and responsive environment, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing needs, enhance product or service quality, and maintain a strong connection with their audience. Integrating feedback loops is instrumental in achieving continuous improvement and staying attuned to the evolving preferences and expectations of stakeholders.
7.Analytics and Reporting:
Analytics and reporting are vital for data-driven decision-making in organizations. Analytics involves systematically analysing data to derive insights, patterns, and trends, helping businesses understand performance, customer behavior, and market dynamics. Reporting presents these insights in a structured format, often through visualizations or summaries. Together, analytics and reporting empower organizations to make informed decisions, track key performance indicators, and assess strategy effectiveness.







.png?h=250&fm=webp)
.png?h=250&fm=webp)
.png?h=250&fm=webp)



.png?h=250&fm=webp)
.png?h=250&fm=webp)
.png?h=250&fm=webp)


.png?h=250&fm=webp)



.png?h=250&fm=webp)
















.png?h=250&fm=webp)

.png?h=250&fm=webp)
.png?h=250&fm=webp)



































































































































.png?h=250&fm=webp)


.jpg?h=250&fm=webp)





 copy.png?h=250&fm=webp)























_ Why do you need one.png?h=250&fm=webp)


























































.jpg?h=250&fm=webp)

.png?h=250&fm=webp)



.png?h=250&fm=webp)

.jpg?h=250&fm=webp)




.png?h=250&fm=webp)









.jpg?h=250&fm=webp)
